Normal Density and Distribution
For a nice regular example we use the celebrated functions Then To obtain quadratic majorizers we must bound the second derivatives. We can bound by setting its derivative equal to zero. We have for , and thus . In the same way for and . At those values . More precisely, it follows that Thus we have the quadratic majorizers and The majorizers are illustrated for both and at the points and in Figures 1 and 2. The inequalities in this section may be useful in majorizing multivariate functions involving and . They are mainly intended, however, to illustrate construction of quadratic majorizers in the smooth case.}
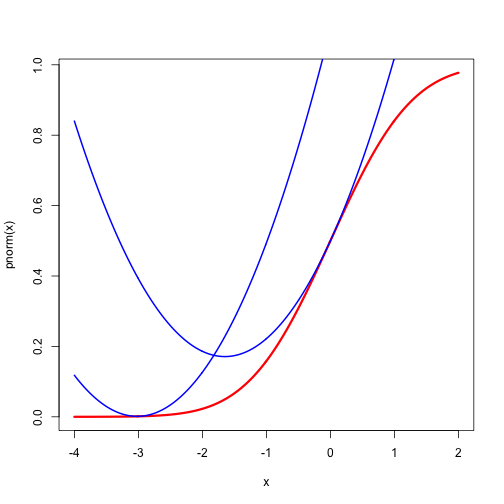
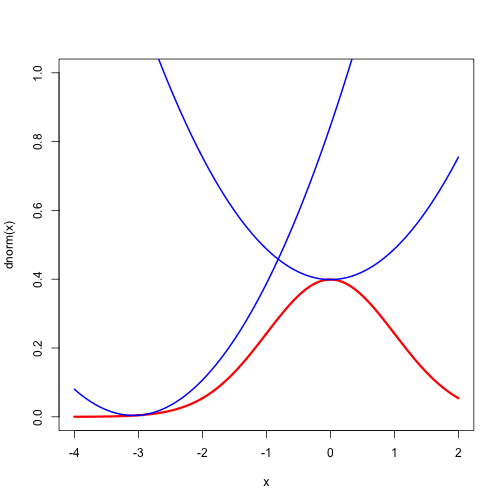
The drawings are made by the code in normal.R.